Description
Eddy Current Magnetic Separators are specialized machines used extensively in the recycling and material processing industries to separate non-ferrous metals from a variety of mixed material streams. Unlike ferrous metal separators, which use magnetic fields to attract metals, Eddy Current Magnetic Separators use the principles of electromagnetic induction to achieve separation.
Principle of Operation

The operation of an Eddy Current Magnetic Separators is based on Faraday's Law of Induction. When a conductor moves through a magnetic field, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced within it. This phenomenon produces circulating currents known as eddy currents. These eddy currents generate their own magnetic field that opposes the original magnetic field, resulting in a repulsive force on the conductor.
Induction of Eddy Currents: As non-ferrous metal particles move through the magnetic field generated by the rotating magnetic drum, eddy currents are induced within these particles.
Generation of Repulsive Force: The induced eddy currents create their own magnetic fields, which interact with the magnetic field of the rotor. This interaction produces a repulsive force.
Separation: The repulsive force propels the non-ferrous metals away from the magnetic rotor, separating them from the rest of the material stream.
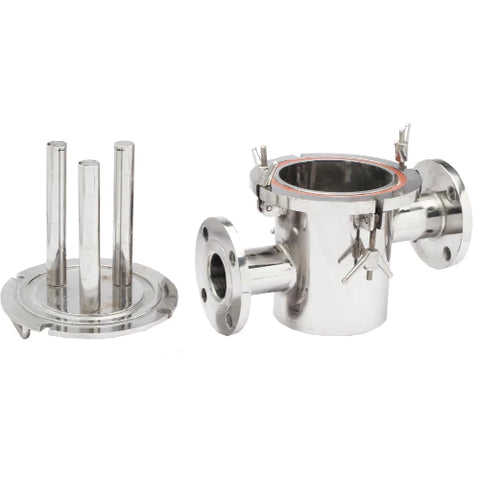
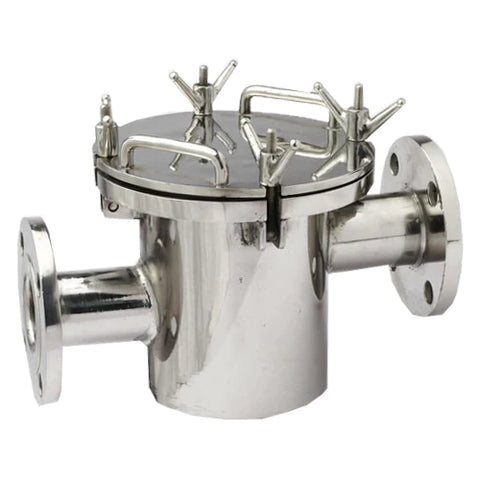
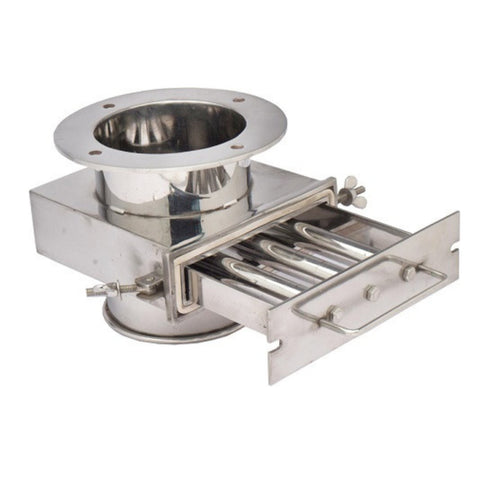
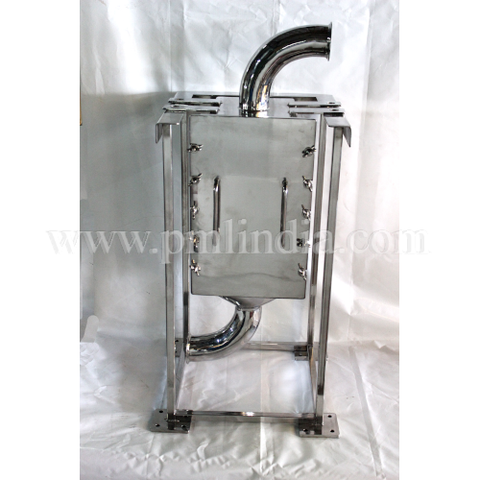
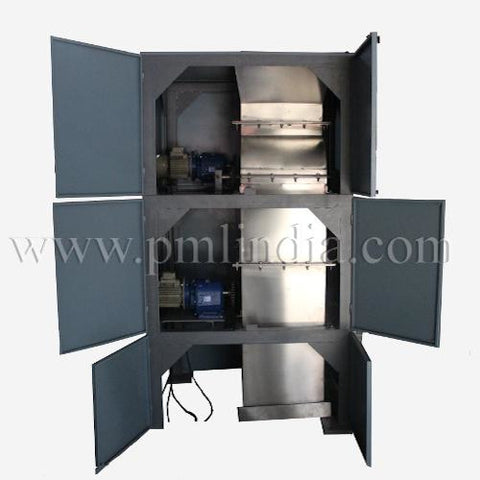
Construction
Eddy Current Magnetic Separators are composed of several key components that work together to achieve efficient separation:
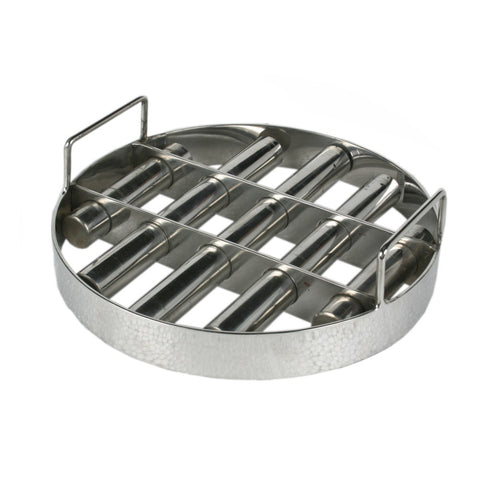
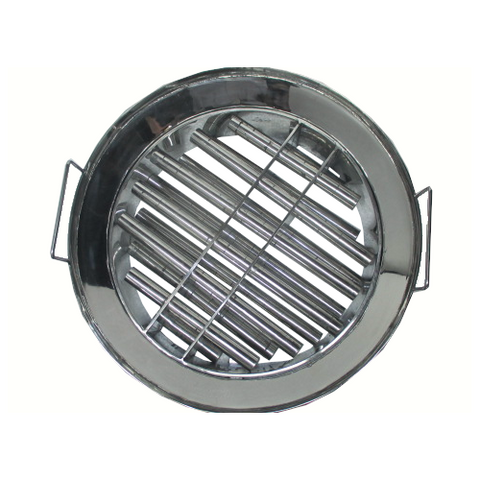
- Conveyor Belt: The conveyor belt transports the mixed material stream towards the magnetic rotor. It is typically made of durable, non-magnetic material to prevent interference with the magnetic fields.
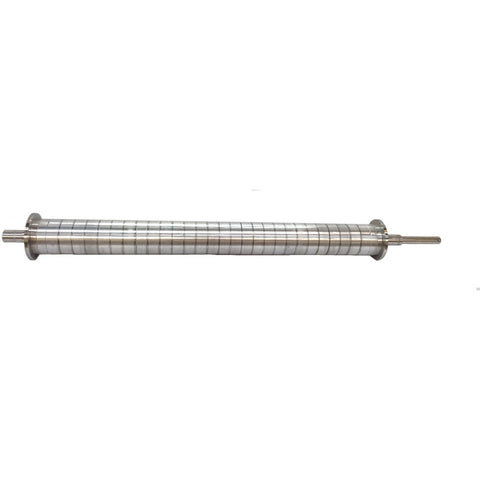
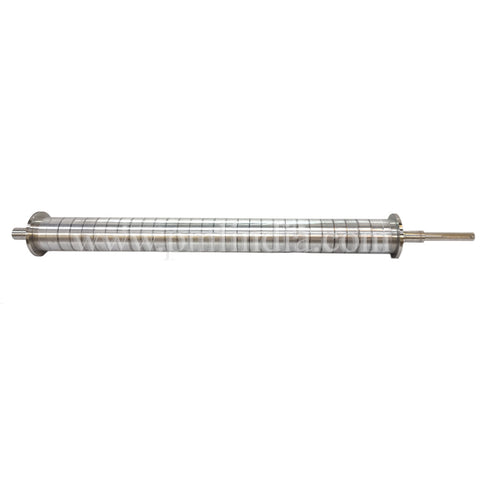
- Magnetic Rotor: This is the heart of the separator. The rotor is equipped with an array of powerful permanent magnets, usually made from rare-earth materials like neodymium. These magnets are arranged in an alternating polarity pattern.
- Drive Mechanism: Powers the conveyor belt and the magnetic rotor. The speed of the rotor can often be adjusted to optimize separation for different materials.
- Splitters: Located at the discharge end, splitters are adjustable barriers that direct separated materials into different collection bins.
- Control System: An electronic control system that regulates the operation of the separator, including the speed of the conveyor belt and magnetic rotor.
How Does It Work?
The process of separation in an Eddy Current Magnetic Separator can be outlined in the following steps:
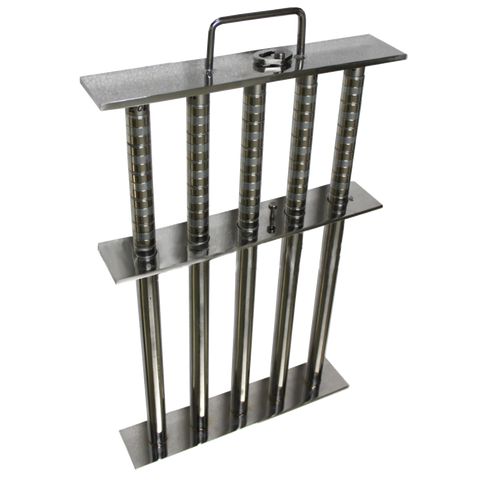
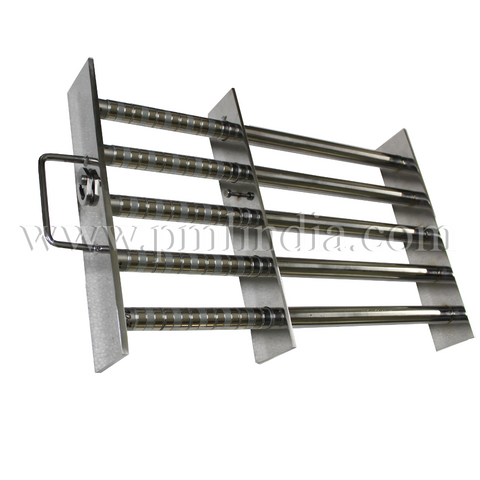
1. Feeding: Mixed materials are fed onto the Vibratory tray feeder, which carries them towards the magnetic drum separator.
2. Magnetic drum separator: Ferrous material is separated from the material feed from Vibratory tray feeder.
3. Conveyor Feeding: Mixed materials are fed onto the conveyor belt, which carries them towards the Eddy current magnetic rotor.
4. Induction Zone: As materials pass over the rapidly rotating magnetic rotor, eddy currents are induced within non-ferrous metal particles.
5. Repulsion: The induced eddy currents generate magnetic fields that repel the non-ferrous metals away from the magnetic rotor.
6. Separation: Due to the repulsive force, non-ferrous metals are ejected from the material stream and separated into a different trajectory, while non-metallic materials continue along the conveyor path and are collected separately.
7. Collection: Separated materials are directed by adjustable splitters into designated collection bins.
Applications
Eddy Current Magnetic Separators are used in a wide range of industries for various applications:
- Recycling Industry: Used extensively to recover non-ferrous metals like aluminium, copper, and brass from municipal solid waste (MSW), electronic waste (e-waste), and other recyclables.
- Automotive Industry: Employed in automotive shredding operations to recover valuable non-ferrous metals from shredded vehicle residues, improving the economic viability of recycling processes.
- Glass and Wood Recycling: Utilized to remove metal contaminants from recycled glass and wood, ensuring higher purity and quality of the final recycled products.
- Foundry Sand Recycling: Used to separate non-ferrous metals from foundry sand, allowing the sand to be reused in the casting process, thereby reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Construction and Demolition Waste: Applied to recover metals from construction and demolition debris, enhancing material recovery and promoting sustainable building practices.
Factors affecting the performance of Eddy Current Magnetic Separator
The performance of Eddy Current Magnetic Separators can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the separation process and achieving maximum efficiency. Here are the key factors affecting the performance of Eddy Current Magnetic Separators -
1. Rotor Speed
2. Magnetic Field Strength
3. Particle Size and Shape
4. Material Feed Rate
5. Material Composition
6. Splitter Position
7. Conveyor Belt Speed
8. Environmental Conditions
9. Equipment Design and Configuration
Advantages of Eddy Current Magnetic Separator
1. High Efficiency
2. Versatility
3. Environmental Benefits
4. Low Maintenance
5. Economic Benefits

Why PML?
- Over 65 years of experience in permanent magnet and system design.
- Custom magnetic systems tailored to client needs.
- Excellent after-sales support, including calibration and audits.